The Office of Technical Assistance is organized along functional lines, operating in five major disciplines.
Revenue Policy and Administration Team
The mission of the Revenue Policy and Administration Program is to provide assistance to tax administrations and ministries of finance in tax administration and tax policy reform. The object of this assistance is increase of revenues consistent with law and with fairness and transparency.
Specific areas of assistance include:
- Tax policy advice and legislative drafting, emphasizing fairness and compliance burden as well as revenue production;
- Efficient tax processing, taxpayer accounting and registration;
- Promotion of tax compliance:
- Support of voluntary compliance through taxpayer education and information;
- Audit and debt management;
- Criminal enforcement;
- Design and management of administrative and organizational systems, including establishing and strengthening of large and medium taxpayer offices;
- Internal controls and internal inspections to deter and redress corruption;
- Effective human resources and performance management systems;
- Project management consulting, particularly with respect to tax IT systems; and
- Training at all levels, from executive strategic planning and management workshops, to technical training of auditors and collectors
Budget and Financial Accountability Team
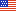
The mission of the Budget and Financial Accountability Program is to strengthen the effectiveness of ministries of finance, the readability and transparency of budget documents, and the management and expenditure of government resources. OTA works with countries to improve all aspects of the “Budget Cycle” depicted below.
 |
|
|---|
The OTA Budget and Financial Accountability Program provides a range of services focusing on the needs of the country. Activities include:
- Reform financial policies and procedures by drafting laws, regulations, standards and manuals;
- Introduce and institutionalize fiscal analytical techniques;
- Implement customized business processes, including manual and automated systems, to improve efficiency and transparency;
- Assist country in meeting international fiscal standards;
- Assess organizational structures, recommend changes resulting in improved workflow, staffing requirements and job descriptions; and
- Increase capacity through informal and formal training.
Government Debt and Infrastructure Finance Team
The mission of the Government Debt and Infrastructure Finance (GDIF) Program is twofold. First, GDIF helps host countries implement sound public debt management practices and develop domestic debt markets through which the government can predictably finance itself within acceptable cost and risk parameters. Robust domestic government debt markets support political and fiscal stability, monetary policy transmission, and broader capital market development for sub-national and private sector issuers and investors. GDIF sovereign debt advisors assist counterpart officials in implementing important objectives:
- Strengthening the legal and regulatory framework for sovereign debt management and issuance;
- Building institutional and staff capacity to issue and manage public debt through market- friendly mechanisms;
- Adopting comprehensive debt management and funding policies and strategies;
- Creating a broader range of financing instruments and sources to fund the government's budgetary and capital investment needs, while providing local investors safe instruments for their savings; and
- Designing and implementing securities issuance, trading and settlement mechanisms that support financial market safety, transparency, efficiency, and liquidity
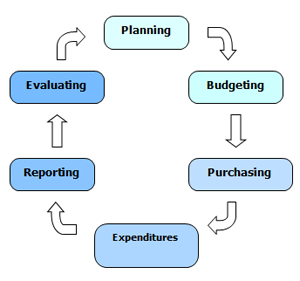
The graphic below illustrates the various components involved in developing domestic financial markets. GDIF operates primarily in the lower three tiers of pyramid, which provide the solid foundation for broader capital market development.
Source: International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Strengthen their legal framework and regulatory environment, particularly for public private partnerships;
- Build and staff an appropriate infrastructure development and management organization;
- Increase their capability to analyze and manage the fiscal impact of specific project proposals, particularly the impact on debt, contingent liabilities and long-term operating costs;
- Improve and institutionalize the project development process, including contracting and dispute resolution mechanisms;
- Enhance interagency and private sector communications; and
- Attract prospective project investors, concessionaires, and creditors.
Banking and Financial Services
The Banking and Financial Services Program supports the development of sound, robust, well-regulated institutions that are effective financial intermediaries accessible to all and resistant to mismanagement, fraudulent financial activity, and adverse macroeconomic conditions. Specific areas of assistance include:
- Corporate Governance: devising structures for central banks and the commercial banking sector.
- Financial Inclusion: promoting access to credit for the bottom of the pyramid (the poorest segment of the population who have traditionally not had access to financial services).
- Financial Stability: harmonizing macro-prudential approaches to monitor financial sector risks; creating oversight committees and issuing financial reports to highlight potential instabilities or weaknesses in financial sectors.
- Emerging Payment Systems: establishment of regulatory frameworks for mobile financial services and innovative approaches to financial market access.
- IT Systems Modernization: design and implementation of core banking, retail payment, and data systems.
- Banking, Insurance, and Financial Market Supervision: implementation of the Basel Accords, risk-based supervision; stress tests and early warning systems.
- Bank Restructuring: rehabilitation of problem banks; management and disposition of distressed assets; liquidation of failed financial institutions; privatization of state-owned banks.
- Deposit Insurance Systems: drafting of laws; operational design; development and implementation of policies and regulations; calculation of fund size and premiums.
- Monetary Policy: analysis of monetary policy, macroeconomic and financial policy; currency issuance and revaluation; establishment of monetary policy research departments.
- Internal Audit and Accounting: adopting and implementing International Financial Reporting Standards; central bank audit functions.
Economic Crimes
The Economic Crimes Team (ECT) promotes compliance with international standards and best practices, including in particular those standards and practices aimed at the establishment of effective anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism (AML/CFT) regimes. As reflected in the illustration below, this broad mission and corresponding systemic approach to technical assistance implicates working relationships with a cross-section of counterpart stakeholders. ECT partners with foreign counterpart regulatory, analytical, law enforcement and judicial authorities tasked in their country with ensuring a safe, sound and transparent financial system; targeting transnational criminal organizations and networks, including their illicit proceeds; and upholding the rule of law.
The ECT supports security sector technical assistance in functional areas to include, among others:
- financial and non-financial (including Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs)) institution regulation and supervision;
- assessments and evaluations;
- counter terrorist financing;
- local, regional and national financial investigative efforts;
- prosecution and judicial functions; and
- financial intelligence unit operations.